CIBR entrance
Lab introduction
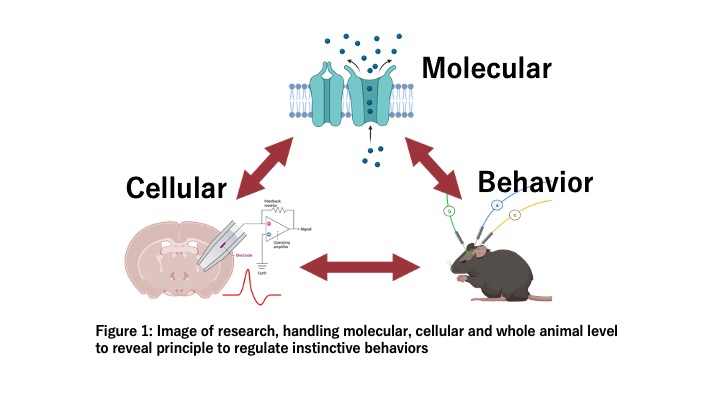
Yamanaka Lab started its activities at CIBR in July 2022. The Yamanaka Lab is engaged in research to elucidate the working principles of the hypothalamic neural circuits that regulate instinctive behaviors such as feeding and drinking behavior, sexual behavior and sleep/wakefulness. Among these instinctive behaviors, our research focuses on the neural circuits involved in sleep/wakefulness regulation. The hypothalamic neurons contain many neurons that produce neuropeptides and release them as neurotransmitters. Recent studies revealed that these peptide-producing neurons are known to play an important role in the regulation of instinctive behaviors. Among them, we are focusing our analysis on neurons that produce neuropeptides, such as orexin and melanin concentrating hormone (MCH)-producing neurons. By clarifying the functional linkage between these hypothalamic neurons and neurons in brain regions that control higher order brain functions such as memory, decision making, emotion, motivation and consciousness, we aim to understand the principles that cause the exhibition of various behaviors and to elucidate the mechanisms of pathological manifestations caused by their functional disruption.
For these studies, we will use mice as model animals and apply molecular biological, electrophysiological, and behavioral pharmacological experimental techniques, handling with molecules, cells, and whole animal level. We aim to elucidate the causal relationship by creating various genetically modified animals, inducing target neuron-specific gene expression by applying viral vectors to them, and analyzing the behaviors that emerge when specific neuronal activities are manipulated by optogenetics and chemogenetics. In addition, we will record neural activities of targeted neurons in animals that are freely behaving under consciousness by using a miniature endoscope (nVista) or fiber photometry. By combining these manipulations and recordings, we try to elucidate detailed causal relationships through conditional perturbations by performing closed-loop operations under various conditions.
We also train the next generation of researchers to conduct these studies. We aim to nurture researchers who not only possess the techniques and knowledge of cutting-edge experiments, but who are also world-class researchers. We aim to nurture researchers who will develop research that clarifies truth, essence, and universality, rather than short-term research.
山中ラボは2022年7月にCIBRにおいて活動を開始しました。山中ラボでは、本能行動を司る視床下部神経回路の動作原理について明らかにする研究を行っています。本能行動の中でも特に睡眠覚醒調節に関わる神経回路に着目しています。視床下部神経の中には、神経ペプチドを産生する神経が数多く存在し、それらの神経が本能行動調節に重要な役割を担うことが知られています。それらの中でも、オレキシン神経、メラニン凝集ホルモン産生神経などの神経ペプチドを産生する神経細胞を中心に解析を行っています。また、これらの視床下部神経と高次脳機能を司る脳領域との機能連関を明らかにすることで、様々な行動発現を引き起こす原理の理解と、その破綻による病態発現のメカニズム解明を目指します。
これらの解明のために、モデル動物としてマウスを用い、分子生物学的、電気生理学的、行動薬理学的な実験手法を適用し、分子、細胞、個体の全てを取扱います。手法としては、様々な遺伝子改変動物を作成し、それらにウイルスベクターを適用することで、標的神経特異的な遺伝子発現を誘導し、光遺伝学や化学遺伝学といった、特定神経の活動を操作する手法を適用した時に現れる行動を解析することで、動作原理の解明を行います。また、超小型内視鏡や、ファイバーフォトメトリーなどによって、意識下に自由行動する動物の特定神経活動記録を行います。これらの操作と記録を組み合わせ、様々な条件下において閉ループ操作による条件的摂動を行い詳細な因果関係の解明を目指します。
また、これらの研究を行うための次世代の研究者の育成も行います。最先端の実験の技術や知識を有するだけで無く、世界的に通用する研究者を育成することを目指しています。目先の研究ではなく、真理・本質・普遍を明らかにするような研究を展開する研究者の育成を目指します。
山中实验室于2022年7月开始在CIBR开展活动。山中实验室从事的研究旨在阐明下丘脑神经回路的工作原理,这些神经回路调节本能行为,如进食和饮水行为、性行为和睡眠/觉醒。在这些本能行为中,我们的研究重点是参与睡眠/觉醒调节的神经回路。下丘脑神经元包含许多产生神经肽并作为神经递质释放的神经元。最近的研究发现,这些产生肽的神经元已知在调节本能行为方面发挥着重要作用。其中,我们的分析重点是产生神经肽的神经元,如食欲素和产生黑色素聚集激素(MCH)的神经元。通过澄清这些下丘脑神经元与控制记忆、决策、情感、动机和意识等高阶大脑功能的脑区神经元之间的功能联系,我们旨在了解导致各种行为展示的原理,并阐明由其功能中断引起的病理表现的机制。
为此,我们使用小鼠作为动物模型,应用分子生物学、电生理学和行为药理学实验技术,处理分子、细胞和个体。这些方法包括创建各种转基因动物,并对其应用病毒载体以诱导目标神经特定的基因表达,以及通过光遗传学和化学遗传学等方法分析操纵特定神经活动时出现的行为,以阐明操作原理。此外,通过超小型内窥镜和纤维光度计,在有意识的条件下自由行动的动物中记录特定的神经活动。结合这些操作和记录,我们旨在通过在各种条件下的闭环操作进行条件性扰动来阐明详细的因果关系。
我们还培训下一代的研究人员来进行这些研究。其目的是培养不仅拥有尖端实验技能和知识,而且还是世界级的研究人员。我们的目标是培养研究人员发展澄清真理、本质和普遍性的研究,而不是短期研究。